Dornier 228 Specifications & Booking
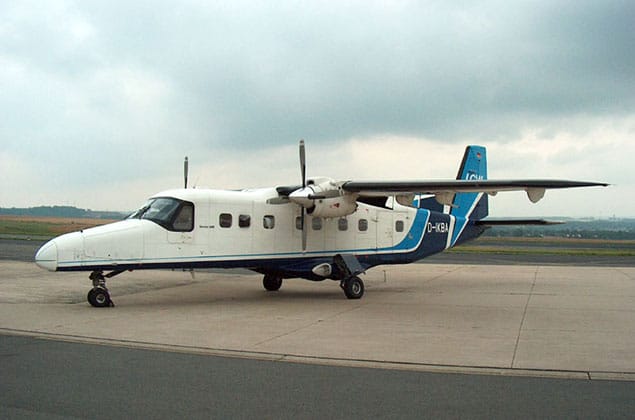
Overview of the Dornier 228
The Dornier 228 is a German-made, twin-turbine, short-takeoff-and-landing (STOL) utility aircraft. Manufactured by Dornier GmbH from 1981 to 1994, it was primarily designed for military and civilian use. The first flight of the Dornier 228 took place on October 27, 1978. One notable milestone in its development is the certification by the German Federal Aviation Administration (Luftfahrt-Bundesamt) in December 1981.
Technical Specifications
The Dornier 228's technical specifications include:
- Dimensions: Length - 16.33 meters, Wingspan - 14.96 meters, Height - 4.63 meters
- Weight: Empty weight - 3,800 kg, Maximum takeoff weight - 6,200 kg
- Engines: Twin Garrett TPE331-10R turboprop engines, each producing 477 kW (645 hp) and with a fuel efficiency of approximately 0.5 kg/kWh
- Performance: Maximum speed - 260 km/h (162 mph), Range - 1,000 km (621 miles), Cruising altitude - 2,500 meters (8,200 ft)
- Capacity: Passengers - 19, Cargo - 1,400 kg (3,086 lbs), Crew - 2
Design and Features
The Dornier 228's design incorporates several innovative features. Its unique STOL capabilities allow it to take off and land on short runways or even grass strips. The aircraft also has a high-lift wing design, which provides excellent lift and maneuverability. Additionally, its fuel-efficient engines and advanced avionics make it an attractive option for military and civilian operators.
History and Development
The development of the Dornier 228 began in the late 1970s as a response to the German military's need for a reliable STOL aircraft. Key milestones include:
- First flight on October 27, 1978
- Certification by the German Federal Aviation Administration (Luftfahrt-Bundesamt) in December 1981
- Entry into service with the German military in 1982
Operational Use
The Dornier 228 has been used by several military and civilian organizations, including:
- Airlines: Lufttransport, Condor Flugdienst, and others operated the aircraft for passenger and cargo transport
- Military: The German Air Force (Luftwaffe) and other nations' air forces used the Dornier 228 for military operations and training
- Popular routes or missions: Military operations, humanitarian aid, search and rescue, and cargo transportation
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known facts about the Dornier 228:
- The aircraft was designed to operate from short runways and unprepared airstrips
- In 1985, a Dornier 228 set a world record for the longest STOL takeoff with a distance of just 100 meters (328 ft)
- The Dornier 228 made its first public appearance at the 1981 Paris Air Show
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes the Dornier 228 unique?
The Dornier 228's STOL capabilities, high-lift wing design, and fuel-efficient engines make it an attractive option for military and civilian operators.
How much does the Dornier 228 cost?
The estimated cost range of a new Dornier 228 is between $1 million to $2.5 million, depending on configuration and customization.
What is the range of the Dornier 228?
The aircraft has a maximum range of approximately 1,000 km (621 miles), making it suitable for short-range missions.
Which airlines operate the Dornier 228?
Airlines such as Lufttransport and Condor Flugdienst have operated the Dornier 228 for passenger and cargo transport. The aircraft was also used by various military organizations.
Is the Dornier 228 still in production?
The Dornier 228 is no longer in production, as manufacturing ceased in 1994. However, some airframes continue to be operated by private and government organizations around the world.